Table of Contents
Main Page
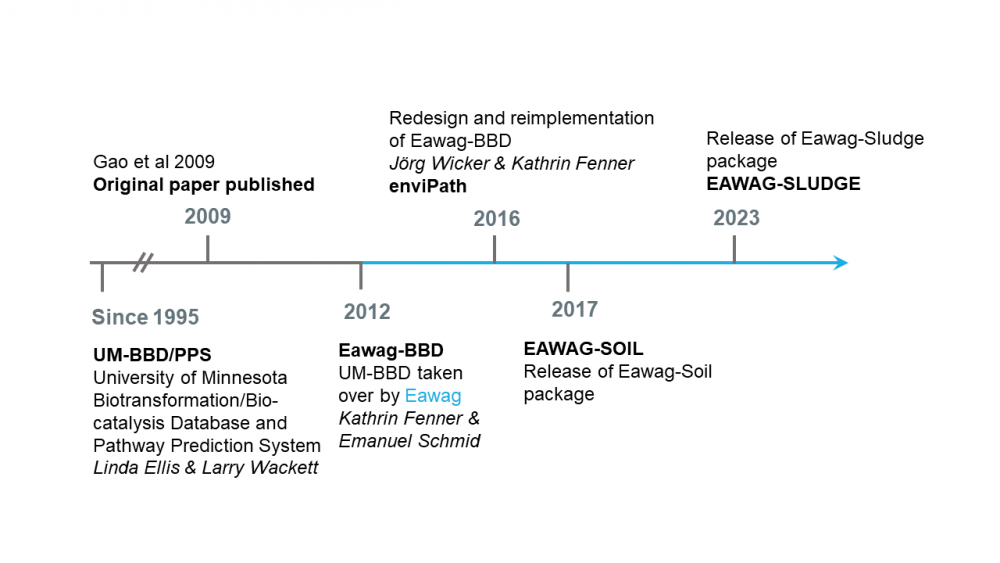
enviPath is an online, publically available database and prediction system for microbially mediated biotransformations of organic environmental contaminants. It is the successor of the University of Minnesota Biocatalysis/Biodegradation Database and Pathway Prediction System (now EAWAG-BBD/PPS) and is a continually evolving product of over 20 years of international scientific collaboration. The enviPath platform provides a thorough, mechanistic understanding and prediction of biotransformation pathways in different experimental and environmental conditions such that academic research teams, consultants, public authorities, and chemical industries can collectively work to reduce harmful chemical contamination in the environment. Below is a brief timeline describing the history of enviPath.
Database
Biotransformation pathways reported in scientific literature as well as predicted or user-entered pathways can all be stored on the database provided within the enviPath platform. You can browse information in the database using the menu on the top banner of start page. The enviPath database is organized into packages, where a user can select which data to access by specifying the package that is most relevant for his/her specific purpose. Each package has an owner who can grant reading or writing permissions. We list data only as reviewed if it is reviewed by one of the organisations or groups in the reviewer group.
Prediction
enviPath can be used to predict biotransformation pathways. You can do this using the input field on the start page by entering a compound in SMILES format, or drawing it using the molecule editor (by clicking on the dropdown on the left), and clicking “Go!”. If the pathway for this compound was has been previously predicted and it is found in the database, a list of corresponding pathways will be returned. Otherwise, the system will generate a new predicted pathway. Note that for anonymous users there is a limit to computation time and size of the predicted pathways. The resulting pathway will be stored in the database for at least 30 days and will be accessible to everyone. Data generated by anonymous users is at risk of getting deleted after 30 days. If you wish to store the pathway for longer, prevent others from changing or seeing your pathways, or use more resources in terms of computation time and size of pathways, please create an account (using the login button) and set appropriate permissions for your packages (default settings should be suitable for most users).
Cite
Cite enviPath
If you use enviPath in your research please cite:
- Hafner, J., Lorsbach, T., Schmidt, S., Brydon, L., Dost, K., Zhang, K., Fenner, K., & Wicker, J (2024). Advancements in Biotransformation Pathway Prediction: Enhancements, Datasets, and Novel Functionalities in enviPath. Journal of Cheminformatics, 16, 93, https://doi.org/10.1186/s13321-024-00881-6
- Wicker, J., Lorsbach, T., Gütlein, M., Schmid, E., Latino, D., Kramer, S., & Fenner, K. (2016). enviPath - The environmental contaminant biotransformation pathway resource. Nucleic Acids Research, 44(D1), D502–D508. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkv1229
Additional literature related to enviPath is listed here
- Gao, J., Ellis, L. B. M., & Wackett, L. P. (2009). The University of Minnesota Biocatalysis/Biodegradation Database: Improving public access. Nucleic Acids Research, 38, 488–491. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkp771
- Latino, D. A. R. S., Wicker, J., Gütlein, M., Schmid, E., Kramer, S., & Fenner, K. (2017). Eawag-Soil in enviPath: a new resource for exploring regulatory pesticide soil biodegradation pathways and half-life data. Environmental Science. Processes & Impacts, 19(3), 449–464. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6em00697c
- Tam, J.Y.C., Lorsbach, T., Schmidt, S., & Wicker,J. (2021). Holistic evaluation of biodegradation pathway prediction: assessing multi-step reactions and intermediate products. Journal of Cheminformatics 13, 63 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13321-021-00543-x
- Trostel, L., Coll, C., Fenner, K., & Hafner, J. (2023). Combining predictive and analytical methods to elucidate pharmaceutical biotransformation in activated sludge. Environmental Science: Processes and Impacts, 25(8), 1322–1336. https://doi.org/10.1039/d3em00161j
- Hafner, J., Fenner, K., & Scheidegger, A. (2023). Systematic Handling of Environmental Fate Data for Model Development─Illustrated for the Case of Biodegradation Half-Life Data. Environmental Science & Technology Letters, 10(10), 859–864. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.estlett.3c00526
- Hafner, J., Lorsbach, T., Schmidt, S., Brydon, L., Dost, K., Zhang, K., Fenner, K., & Wicker, J. S. (2023). Advancements in Biotransformation Pathway Prediction: Enhancements, Datasets, and Novel Functionalities in enviPath. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-3607847/v1
- Zhang, K., & Fenner, K. (2023). enviRule: an end-to-end system for automatic extraction of reaction patterns from environmental contaminant biotransformation pathways. Bioinformatics, 39(7). https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btad407
- Karakurt-Fischer, S., Johnson, D. R., Fenner, K., & Hafner, J. (2023). Making waves: Enhancing pollutant biodegradation via rational engineering of microbial consortia. Water Research, 247, 120756. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2023.120756
- Dost, K., Pullar-Strecker, Z., Brydon, L., Zhang, K., Hafner, J, Riddle, P., & Wicker, J (2023). Combatting over-specialization bias in growing chemical databases. Journal of Cheminformatics, 15, 53. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13321-023-00716-w
Changelogs
Documentation
REST API
Data Upload
We are working to upload biotransformation pathways in a quick and efficient manner using an excel workbook. If you want to add your data to a future reviewed package, please fill out this template envipath_upload_template_2025.xlsx and upload your completed version to our Dropbox folder. Note- when you upload your filled-out version, you will need to rename it to something unique (i.e. lastname_firstname_yymmdd_compoundname.xlsx)
Associated Resources
ContaHMM: A Resource for the search of Biotransformation-Related Bacterial Genes
We present a dataset and HMMs (Hidden Markov Models) for biotransformation-related bacterial genes, compiled from existing databases and enhanced by extensive metadata collection, manual curation, and HMM generation.This collection aims to facilitate the annotation of biotransformation-related enzymes and expand the known examples in the field.
